| Issue |
EPL
Volume 128, Number 6, December 2019
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 67001 | |
| Number of page(s) | 7 | |
| Section | Condensed Matter: Electronic Structure, Electrical, Magnetic and Optical Properties | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/128/67001 | |
| Published online | 05 February 2020 | |
Wavelength-selective, tunable and switchable plasmonic perfect absorbers based on phase change materials Ge2Sb2Te5
1 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhengzhou University of Aeronautics - Zhengzhou 450046, China
2 Henan Key Laboratory of Aeronautical Material and Application Technology - Zhengzhou 450046, China
3 College of Physics and Optoelectronics, South China University of Technology - Guangzhou 510640, China
(a) dingpei@zua.edu.cn
(b) phzyli@scut.edu.cn
Received: 25 August 2019
Accepted: 26 December 2019
Nanoscale active devices, such as all-optical modulators and electro-optical transducers, can be implemented in heterostructures that integrate plasmonic nanostructures with functional active materials. Here, we demonstrate control over absorption properties in such a heterostructure by coupling the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) of gold nanoantennas to a phase change material (PCM), Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST). The peak absorption of this hybrid absorber approaches near unity at resonance due to the simultaneous excitations of electric and magnetic resonant modes. Moreover, such a hybrid absorber can realize arbitrary wavelength-selective spectral absorption in the mid-infrared region simply by altering the square nanoantennas side length. By controlling the total power of the incident light, the intermediate phases composed of different proportions of the amorphous and crystalline molecules of the GST can be correspondingly tailored, and thus the absorption can be continuously tuned, which provides a flexible and encouraging way to achieve active features once fabricated. Importantly, by converting GST from the amorphous to crystalline state or vice versa, the hybrid absorber can realize bidirectional switching of “ON” and “OFF” states, with an outperformed modulation depth of 98% (or 95%) and extinction ratio of  (or
(or 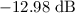 ), respectively, indicating its excellent optical modulation performance. Notably, all the stable and intermediate phases of the GST are stable at room temperature, and therefore no sustained external thermal consumption is needed to maintain a desired absorption band for the hybrid scheme. Additionally, the structure can tolerate a wide range of incident angles as well as show polarization-independent features. With these extraordinary optical responses, the proposed scheme could find potential applications in active photonic devices such as optical modulation, thermal imaging and optical switching.
), respectively, indicating its excellent optical modulation performance. Notably, all the stable and intermediate phases of the GST are stable at room temperature, and therefore no sustained external thermal consumption is needed to maintain a desired absorption band for the hybrid scheme. Additionally, the structure can tolerate a wide range of incident angles as well as show polarization-independent features. With these extraordinary optical responses, the proposed scheme could find potential applications in active photonic devices such as optical modulation, thermal imaging and optical switching.
PACS: 78.20.-e – Optical properties of bulk materials and thin films / 42.79.-e – Optical elements, devices, and systems
© EPLA, 2020
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


