| Issue |
Europhys. Lett.
Volume 56, Number 5, December 2001
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 722 - 728 | |
| Section | Condensed matter: electronic structure, electrical, magnetic, and optical properties | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1209/epl/i2001-00580-y | |
| Published online | 01 December 2003 | |
Electronic-structure modifications induced by surface segregation
in  thin films
thin films
1
Department of Physics and Astronomy and the
Center for Material Research and Analysis, Behlen Laboratory,
University of Nebraska Lincoln, NE 68588-0111, USA
2
Material Physics Branch, Naval Research
Laboratory - Washington DC 20375, USA
Corresponding author: pdowben@unl.edu
Received:
11
July
2001
Accepted:
20
September
2001
Using spin-polarized inverse photoemission and X-ray absorption
spectroscopy techniques, we show that the electronic structure of
 thin films depends on the composition at the
surface. With a gentle annealing procedure, the surface provides a
maximum of 80% spin asymmetry at 0.5
thin films depends on the composition at the
surface. With a gentle annealing procedure, the surface provides a
maximum of 80% spin asymmetry at 0.5 above the Fermi level
in spite of extensive
above the Fermi level
in spite of extensive  segregation. A heavily annealed
(restructured) surface exhibits a reduced surface "ordering"
temperature of 240
segregation. A heavily annealed
(restructured) surface exhibits a reduced surface "ordering"
temperature of 240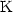 (compared to the approximately 335
(compared to the approximately 335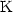 bulk value) as well as a reduced spin asymmetry value of 40% at
0.5
bulk value) as well as a reduced spin asymmetry value of 40% at
0.5 above Fermi energy.
above Fermi energy.
PACS: 73.20.-r – Electron states at surfaces and interfaces / 68.35.Fx – Diffusion; interface formation / 75.25.+z – Spin arrangements in magnetically ordered materials (including neutron and spin-polarized electron studies, synchrotron-source X-ray scattering, etc.)
© EDP Sciences, 2001
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


