| Issue |
Europhys. Lett.
Volume 64, Number 5, December 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 592 - 598 | |
| Section | General | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1209/epl/i2003-00269-3 | |
| Published online | 01 November 2003 | |
Quantum oligopoly
1
Department of Physics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong Shatin, New Territories, Hong Kong
2
Department of Natural Sciences, National Institute of Education Nanyang Technological University - 1 Nanyang Walk, Singapore 637616
Corresponding authors: cflo@phy.cuhk.edu.hk dkiang@nie.edu.sg
Received:
13
May
2003
Accepted:
6
October
2003
Based upon a modification of Li et al. 's “minimal” quantization
rules (Phys. Lett. A306(2002) 73), we investigate the
quantum version of the Cournot and Bertrand oligopoly. In the
Cournot oligopoly, the profit of each of the N firms at the
Nash equilibrium point rises monotonically with the measure of
the quantum entanglement. Only at maximal entanglement, however,
does the Nash equilibrium point coincide with the Pareto optimal
point. In the Bertrand case, the Bertrand Paradox remains for
finite entanglement (i.e., the perfectly competitive
stage is reached for any  ), whereas with maximal
entanglement each of the N firms will still have a non-zero
shared profit. Hence, the Bertrand Paradox is completely
resolved. Furthermore, a perfectly competitive market is reached
asymptotically for
), whereas with maximal
entanglement each of the N firms will still have a non-zero
shared profit. Hence, the Bertrand Paradox is completely
resolved. Furthermore, a perfectly competitive market is reached
asymptotically for 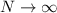 in both the Cournot and
Bertrand oligopoly.
in both the Cournot and
Bertrand oligopoly.
PACS: 03.67.-a – Quantum information / 02.50.Le – Decision theory and game theory
© EDP Sciences, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


