| Issue |
EPL
Volume 136, Number 2, October 2021
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 27003 | |
| Number of page(s) | 4 | |
| Section | Condensed Matter: Electronic Structure, Electrical, Magnetic and Optical Properties | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/ac4528 | |
| Published online | 04 February 2022 | |
Towards high-performance near-infrared photodetectors based on SnS nanowires
1 College of Optical and Electronic Technology, China Jiliang University - Hangzhou 310018, China
(a) yqpeng@cjlu.edu.cn (corresponding author)
(b) shuhaibo@cjlu.edu.cn
Received: 7 August 2021
Accepted: 21 December 2021
Compared with bulk structures, semiconductor nanowires exhibit a higher surface-to-volume ratio, as well as unique electrical and optical properties. Due to its narrow band gap, tin (ii) sulfide (SnS) nano wire is a promising candidate for constructing near-infrared (NIR) photodetectors. Uniformly distributed and well-aligned SnS nanowires were grown on a mica substrate by chemical vapor deposition, and NIR photodetectors with Au (Au-device) and Al (Al-device) as the electrode were fabricated and characterized. Compared to the Au-device, the Al-device achieved higher photodetectivity due to reduced dark current. More importantly by incorporating a photosensitive lead phthalocyanine (PbPc) film into the Al-device, both responsivity and detectivity could be apparently improved, especially at weak light intensities. Under a weak light intensity of 0.79 mW/cm 2the photoresponsivity and specific detectivity were improved from 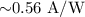 and
and 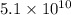 Jones to 0.96 A/W and
Jones to 0.96 A/W and 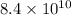 Jones, respectively.
Jones, respectively.
© 2022 EPLA
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


