| Issue |
EPL
Volume 139, Number 5, September 2022
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 51002 | |
| Number of page(s) | 7 | |
| Section | Statistical physics and networks | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/ac86f2 | |
| Published online | 24 August 2022 | |
From normal to anomalous diffusion of water molecules in narrow carbon nanotubes with defects, gases, and salts
1 Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences - Shanghai 201800, China
2 Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Zhangjiang Laboratory, Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences - Shanghai 201210, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences - Beijing 100049, China
(a) chenjige@zjlab.org.cn (corresponding author)
Received: 23 May 2022
Accepted: 4 August 2022
In this letter, we study the diffusion of water molecules inside narrow carbon nanotubes in the presence of nanotube defects, gas molecules and salt ions by using molecular dynamics simulations. Mean square displacement (MSD) with a power-law fitting parameter 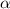 , and the probability distribution function (PDF) with an
, and the probability distribution function (PDF) with an  distribution parameter a, of water molecules are calculated. It is found that within the diffusion time scale, water molecules exhibit a superdiffusion behavior with
distribution parameter a, of water molecules are calculated. It is found that within the diffusion time scale, water molecules exhibit a superdiffusion behavior with 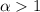 inside a perfect nanotube and the superdiffusion is weakened in the presence of gas molecules and salt ions. Meanwhile, a normal diffusion behavior with
inside a perfect nanotube and the superdiffusion is weakened in the presence of gas molecules and salt ions. Meanwhile, a normal diffusion behavior with 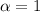 is observed inside a defective nanotube, and it is replaced by a subdiffusion behavior with
is observed inside a defective nanotube, and it is replaced by a subdiffusion behavior with 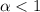 when gas molecules and salt ions are involved. PDF of water molecules is found to be Gaussian-like with
when gas molecules and salt ions are involved. PDF of water molecules is found to be Gaussian-like with 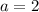 subject to superdiffusion and normal diffusion, while it becomes a center-peaked and long-tailed Lévy distribution with a < 2 subject to subdiffusion. Furthermore, it is found that the diffusion behavior of water molecules approaches normal diffusion as the radius size of the nanotube increases. Our result implies anomalous transport behavior of water in nanochannels due to the common presence of defects, gases and salts in nanochannels.
subject to superdiffusion and normal diffusion, while it becomes a center-peaked and long-tailed Lévy distribution with a < 2 subject to subdiffusion. Furthermore, it is found that the diffusion behavior of water molecules approaches normal diffusion as the radius size of the nanotube increases. Our result implies anomalous transport behavior of water in nanochannels due to the common presence of defects, gases and salts in nanochannels.
© 2022 EPLA
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


