| Issue |
EPL
Volume 143, Number 5, September 2023
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 59004 | |
| Number of page(s) | 6 | |
| Section | Gravitation, cosmology and astrophysics | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/acf60c | |
| Published online | 21 September 2023 | |
Model selection with baryonic acoustic oscillations in the Lyman-α forest
Department of Physics, The Applied Math Program, and Department of Astronomy, The University of Arizona Tucson, AZ 85721, USA
(a) E-mail: fmelia@email.arizona.edu (corresponding author)
Received: 11 April 2023
Accepted: 1 September 2023
The recent release of the final, complete survey of Lyman-α baryonic acoustic oscillation measurements provides the most significant and accurate data base for studying cosmic geometry at an effective redshift 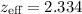 , which is inaccessible to other sources. In this paper, we use these data to select among four distinct cosmologies: Planck ΛCDM, the
, which is inaccessible to other sources. In this paper, we use these data to select among four distinct cosmologies: Planck ΛCDM, the  universe, the Milne universe and the Einstein-de Sitter universe. Given the breadth and depth of the Lyman-α study, this BAO measurement alone provides a strong model comparison, complementary to previous studies that combined Lyman-α data with measurements at lower redshifts. Though both approaches are useful, the latter tends to dilute the disparity between model predictions and the observations. We therefore examine how the models compare to each other strictly based on the BAO scale measured in the Lyman-α forest and background quasars. We find that the Milne universe and the Einstein-de Sitter universe are strongly ruled out by these data. There is also strong evidence disfavoring the standard model. The Lyman-α measurements are completely consistent with the cosmic geometry predicted by
universe, the Milne universe and the Einstein-de Sitter universe. Given the breadth and depth of the Lyman-α study, this BAO measurement alone provides a strong model comparison, complementary to previous studies that combined Lyman-α data with measurements at lower redshifts. Though both approaches are useful, the latter tends to dilute the disparity between model predictions and the observations. We therefore examine how the models compare to each other strictly based on the BAO scale measured in the Lyman-α forest and background quasars. We find that the Milne universe and the Einstein-de Sitter universe are strongly ruled out by these data. There is also strong evidence disfavoring the standard model. The Lyman-α measurements are completely consistent with the cosmic geometry predicted by  . As such, evidence continues to grow that the zero active mass condition from general relativity ought to be an essential ingredient in ΛCDM.
. As such, evidence continues to grow that the zero active mass condition from general relativity ought to be an essential ingredient in ΛCDM.
© 2023 The author(s)
 Published by the EPLA under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY). Further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the published article's title, journal citation, and DOI.
Published by the EPLA under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY). Further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the published article's title, journal citation, and DOI.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


